A research team from the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), and Tsinghua University has developed a new mRNA vaccine delivery method that could improve safety, enhance effectiveness, and reduce patient burden.
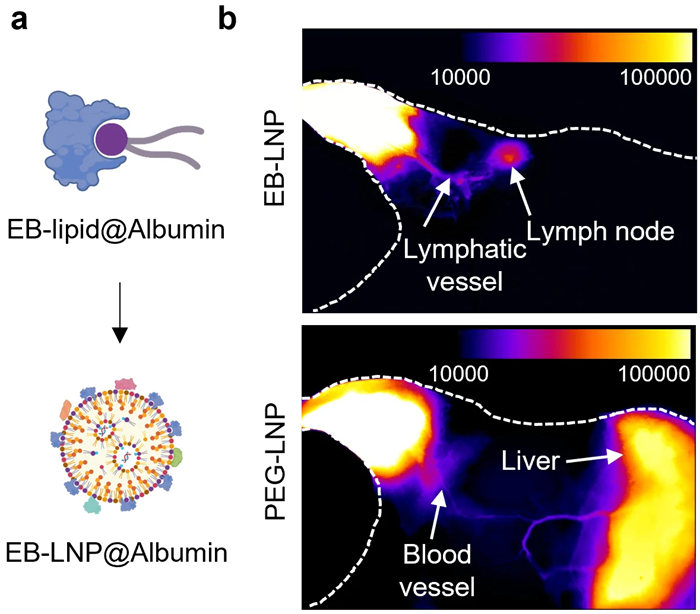
Published in Nature Materials, the study introduces a technique that uses albumin-recruiting lipid nanoparticles—known as Evans Blue-modified lipid nanoparticles (EB-LNPs)—to deliver mRNA directly to the lymph nodes, the immune system’s key hubs. Unlike current delivery systems, which often accumulate in the liver and may trigger toxicity, this new approach largely bypasses the liver.
In lab tests, the EB-LNP delivery system outperformed traditional methods across several applications, including cancer immunotherapy and protection against viral infections such as melanoma, HPV-related cancers, H1N1 influenza, and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2.
Traditional lipid nanoparticle-based vaccines can accumulate in the liver after intramuscular injection, raising the risk of liver damage and dampening immune responses. We aimed to design a smarter delivery system that avoids this problem and directs the vaccine exactly where it’s needed.
Shawn Chen Xiaoyuan, Study Co-Senior Author and Professorm, Department of Diagnostic Radiology, and Nanomedicine Translational Research Programme, National University of Singapore
While current polyethylene glycol-lipid nanoparticles (PEG-LNPs) are widely used for mRNA delivery, they often get trapped in the liver, which is especially problematic when high or repeated doses are required, as in cancer treatment. This can lead to inflammation, allergic reactions, or liver toxicity.
To address this, the team opted to use albumin, a naturally occurring transport protein, to guide the vaccine payload through the lymphatic system directly to the lymph nodes.
The researchers developed a delivery system that uses albumin—a naturally occurring transport protein—to guide the vaccine through the lymphatic system directly to the lymph nodes. By “hitchhiking” on albumin, the vaccine reaches its target efficiently, where it’s absorbed and prompts a focused, robust immune response.
To achieve this, the team synthesized a specialized EB-lipid that binds tightly to albumin. Once injected into muscle tissue, the resulting EB-LNPs attract albumin to their surface, which naturally steers them toward lymph nodes rather than the liver. This design avoids broad systemic circulation, significantly reducing liver exposure and the risk of toxicity.
Even at lower doses, the EB-LNP vaccines triggered strong antitumor T-cell activity and high levels of neutralizing antibodies. Importantly, no liver inflammation or toxic effects were observed, even with repeated injections. And unlike conventional PEG-LNPs, EB-LNPs did not provoke strong anti-drug antibody responses.
This albumin-hitchhiking strategy represents a paradigm shift in mRNA vaccine delivery. It has broad implications for cancer, infectious diseases, and potentially autoimmune disorders. For patients, that means fewer injections, reduced side effects, and longer-lasting protection.
Guocan Yu, Assistant Professor, Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University
Looking ahead, the research team is preparing to move into clinical trials to assess safety and efficacy in humans. They also plan to explore broader applications, including treatments for autoimmune diseases and lymphatic cancers. In parallel, they’re working with industry partners to scale up manufacturing and speed up the development of this next-generation mRNA vaccine platform.
Our hope is to transform how mRNA vaccines are designed—making them safer, more effective, and easier to administer.
Pei Huang, Study Co-Lead Author, and Research Fellow, Department of Diagnostic Radiology, and Nanomedicine TRP, National University of Singapore
Journal Reference:
Feng, Y., et al. (2025) Albumin-recruiting lipid nanoparticle potentiates the safety and efficacy of mRNA vaccines by avoiding liver accumulation. Nature Materials. doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02284-w
Source:


